
#Part of the brain that controls emotion series
The amygdala (aka amygdaloid) is the almond-shape series of neural circuits located deep in the brain’s temporal lobe. – Doc Childre & Deborah Rozman, Transforming Anxiety: The HeartMath Solution for Overcoming Fear & Worry & Creating Serenity You can be operating like a split-screen, your rational or conceptual mind saying one thing and your feelings another because of stored emotional histories. These emotional histories will condition how you feel and react to situations now. Strong emotional experiences become your body’s emotional history. The amygdala constructs reality-based on emotional patterning from the past, which colors your current perceptions and reactions. This area of the brain is involved in emotional processing and regulating behavior.
#Part of the brain that controls emotion skin
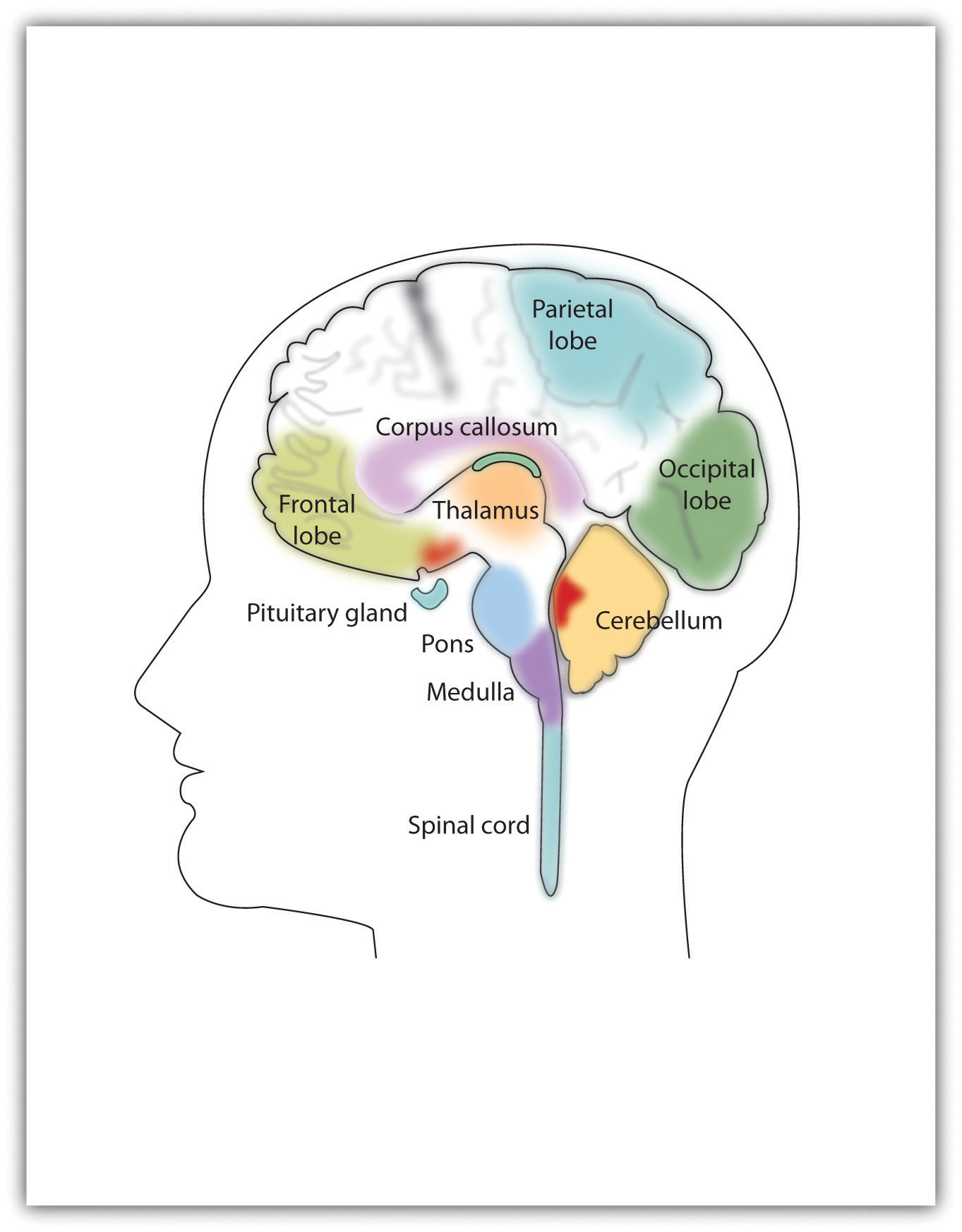
(1)Īfter receiving the signals from your eyes, ears, tongue, and skin it relays that information to both pathways, the cerebral cortex (the outermost part of the brain) and the amygdala. The Thalamus collects everything that your senses pick up from your environment, with the exception of your olfactory input – everything you see, hear, taste, and touch. In this context, you can think of your Thalamus as a ‘switching station’ or a ‘filtering gate’ whose job is to distribute every bit of incoming information from the outside world. The Thalamus plays an important role in the information processing circuit related to your anxious thoughts and reactions.

The hypothalamus works closely with the pituitary gland – an endocrine gland that regulates hormones such as stress hormones and oxytocin aka “the love hormone.”Īcts like a two-way relay station processing and directing information from the spinal cord to the middle brain and up to the cerebrum and then from the cerebrum down the spinal cord to the nervous system. Interacts with the endocrine system (hormonal system) to maintain homeostasis (bodily balance). It helps us stay in the present moment by helping to convert short term memory into long-term memory. The following form part of the limbic system: The limbic brain controls emotions and influences the endocrine ( hormonal) system and the autonomic nervous system. This network is found in the middle brain (underneath the cerebrum). Known as the Limbic system, this part of the brain oversees learning, memory, processing emotions, and activates the fight or flight response ( stress response) in reaction to perceived dangers, painful situations, and threats. It is comprised of the brain stem – at the base of the head – and is connected to the spinal cord.Ģ – The Emotional Brain: (source: ) Known as the “Reptilian brain” oldest structure and it oversees our most basic functions like heart rate, body temperature, blood pressure, digestion, sleeping, and breathing rate. It’s astonishing to think that this mass made up of over 86 billion neurons (brain cells) has been evolving over time and is comprised of three distinct brain structures or networks that emerged along the evolutionary path of humankind.Īccording to the Triune Brain theory, these three distinct areas of the brain can be thought of as three brains in one:ġ – The Primitive Brain: (source: Chuck Pettis via Medium) The human brain is one of the most complex networks in the universe. They’re there to be engaged and expressed with imagination and intelligence. Our feelings are not there to be cast out or conquered.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
